- Opening Hours
- Timing: Mon to Sat - 10 AM to 5 PM
- Address: Positron Hospital, Health Center Plot Block B Suncity, Sector 35, Suncity Township-I, Rohtak, Haryana 124001
- Call Us+123-456-78-09
- Opening Hours
- Timing: Mon to Sat - 10 AM to 6 PM
- Address: Positron Hospital, Health Center Plot Block B Suncity, Sector 35, Suncity Township-I, Rohtak, Haryana 124001
Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction is the persistent difficulty achieving or maintaining an erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance. It is a common condition, especially with advancing age, but can affect men of any age. ED often signals underlying health issues and impacts quality of life, self-esteem, and relationships. Causes are usually multifactorial, involving vascular, neurological, hormonal, psychological, or medication-related factors. Early evaluation by a urologist or andrologist is recommended for proper diagnosis and management.
Here are anatomical illustrations showing the mechanism of erection, including blood flow into the corpora cavernosa:
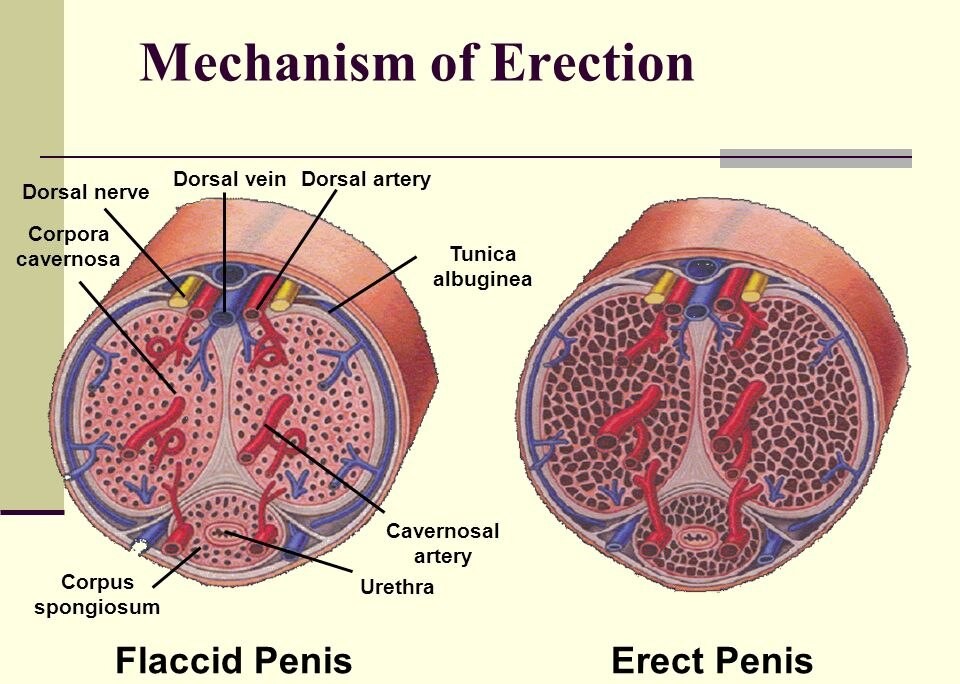
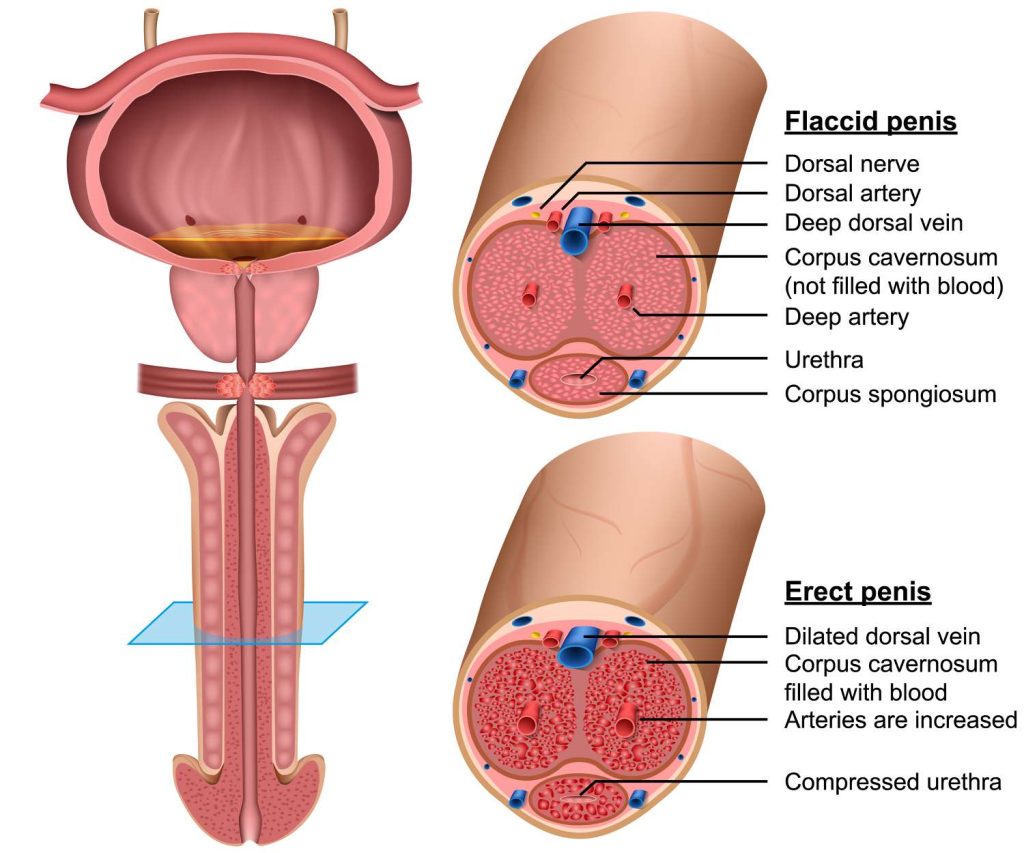
This cross-section highlights the penis structure during flaccid and erect states:
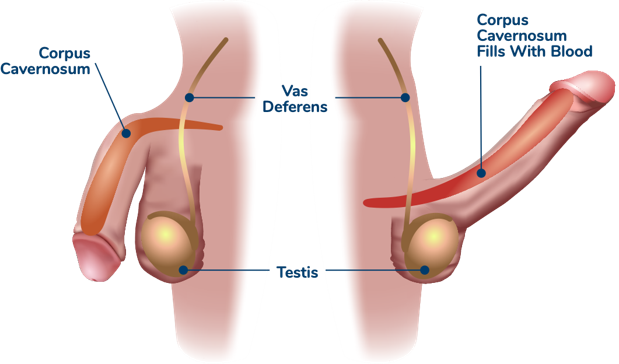
Conservative and Lifestyle Management for Mild to Moderate ED
Initial treatment focuses on lifestyle modifications and addressing reversible causes. Adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle: regular aerobic exercise, balanced diet rich in fruits/vegetables, weight management, smoking cessation, and limited alcohol intake. These improve vascular health and often enhance erectile function.
Pelvic floor muscle exercises (Kegels for men) strengthen the muscles supporting erection and ejaculation. Practice by contracting the muscles used to stop urine flow midstream, holding for several seconds, then relaxing. Repeat regularly.
Manage stress, anxiety, or depression through counseling, mindfulness, or therapy, as psychological factors play a major role in many cases. Review medications with a doctor, as some (e.g., antihypertensives, antidepressants) can contribute.
Medical and Advanced Treatments for Persistent ED
When lifestyle changes are insufficient, proven treatments include oral PDE5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil, tadalafil), which enhance blood flow by relaxing penile smooth muscle during sexual stimulation.
Other options include vacuum erection devices (penis pumps) that draw blood into the penis with a constriction ring to maintain erection.
